There is increasing evidence for antigen-driven B-cell receptor (BCR) signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and other lymphoid malignancies. This includes antigens from infections e.g.Helicobacter pyloriand Hepatitis C virus, but it is theorised that self-antigens may play a major role in some cases of lymphoid malignancy. IgVH4-34 demonstrates intrinsic autoreactivity to self-antigens on red cells, which appears to be largely mediated by two motifs within the first framework region (FR1); Q6W7 and A24V25Y26. These motifs work together to for a hydrophobic patch which determines red cell antigen binding and are frequently mutated away from self-reactivity in normal B cells. IgVH4-34 has been reported to be over-represented in DLBCL compared with expression in normal B cells.
We therefore sought to identify IgVH4-34 DLBCL cases from a local cohort and to screen them for Q6W7 and A24V25Y26 motifs expecting them to be less frequently mutated in DLBCL compared with normal B cells.We also aimed to screen V4-34 cases for associated somatic mutations in other genes using high-throughput sequencing.
DLBCL patient samples were obtained via the Haematology Research Tissue Bank (HRTB) in Canberra, Australia, and the Victoria Cancer BioBank. Forty-eight Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) samples and 26 fresh frozen samples were screened. All samples were collected at the time of diagnosis. Patients were treated with standard chemoimmunotherapy approaches.
IgVH 4-34 gene sequences were determined using an IgVH4 family-specific leader primer in combination with a JH consensus reverse primer. The IgVH region was then sequenced using Sanger sequencing. Sequences were analyzed using the IgBLAST database (National Centre for Biotechnology Information).
DNA extracted from FFPE samples generally proved to have low concentration and fragmented DNA. Only 1 IgVH4-34 sequence was obtained from FFPE tissue.
Five samples sequenced from fresh tissue were identified as using IgVH4-34. Using Hans criteria, it was possible to classify 3 of the 6 cases as germinal center (GC) and 1 as non-GC origin.
Using fresh samples, we estimated the frequency of IgVH4-34 cases at 23%.
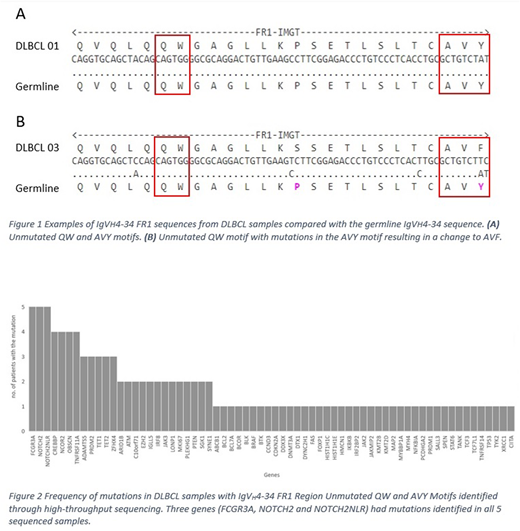
Within FR1, Q6W7 was unmutated in all 6 samples.
One sample had mutations in the A24V25Y26 motif resulting in a change to A24V25F26. The other 5 samples (83.3%) had unmutated AVY motifs.
We extracted genomic DNA from and performed next generation sequencing on the 5 samples with unmutated Q6W7 and A24V25Y26 motifs using a customized capture library (SureSelectXT Target Enrichment System, Aqilent Technologies) covering genes involved in lymphomagenesis. The purified libraries were sequenced on the Illumina NextSeq500 platform at AGRF (Australian Genome Research Facility, Australia).
Several genes (FCGR3A,NOTCH2andNOTCH2NLR) had mutations in all 5 samples.FCGR3Ais an IgG Fc receptor gene, and mutations inFCGR3Ahave previously been linked to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).NOTCH2pathway genes are frequently mutated in DLBCL.CREBBPwas mutated in four of the five samples. Mutations inCREBBPhave previously been linked with DLBCL development and regulation of immune responses.
We identified high rates of IgVH4-34 (23%) in our cohort of fresh samples as previously reported. Further, we noted preservation of the Q6W7 and A24V25Y26 motifs in IgVH4-34-expressing DLBCL. This over-representation of unmutated FR1 motifs suggests that the ability to recognise self-antigens likely provides important ongoing BCR signalling that promotes survival in DLBCL.
This study also highlights the difficulties in conducting DNA-based research on FFPE clinical samples which have not been collected for research purposes and the importance of tissue banking fresh samples.
Studies are currently being conducted into the efficacy of BCR pathway inhibitors e.g. ibrutinib in the treatment of DLBCL and testing for unmutated IgVH4-34 FR1 motifs may present a method to predict patients who are more likely to respond.
Mutations in genes such as FCGR3A,NOTCH2andCREBBPmay work in conjunction with the preserved QW and AVY motifs to promote lymphomagenesis in IgVH4-34-expressing B cells and may present targets for future research into treatment therapies.
Talaulikar:Roche:Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding;Janssen:Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau;Amgen:Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding;Takeda:Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal